

WHAT DOES THE HFS FILE SYSTEM LOOK LIKE WINDOWS
Windows has partitions such as C: and D.Įach program or binary uses specific libraries to function and the /lib directory is where these libraries can be located. This concept is not unique to Linux, as the same thing can be observed in other Operating Systems such as a very interesting one you may have heard of called Windows. Though it is separate from “/root directory”, so you shouldn’t confuse the two.Īll other directories stem from this top level directory like a pyramid. The name “top level” means the “root”, thus it is the root directory of the system. is the top level directory of a Linux system. You should now be able to ascertain which file system you currently have mounted on your Linux distro. (shown below)Īs you can see, in the second column under “Type” the file system type is defined. It will display the file system type along with other currently irrelevant information. Well, that is where this interesting little option comes in: open your terminal and execute this command: $ df -T Now, you may have noticed that I mentioned that this command can be used to define the file system mounted, but when you run the “df” command yourself, there is no mention of any types of file systems. It’s particularly noteworthy for how incredibly well it works with very large files. XFS: xfs, an acronym that stands for “Extent File System”, was created by Silicon Graphics and originally made for their OS “IRIX”, but was later given to Linux.Ĭreated in 1990, XFS is a 64-bit high performance journaling file system. What’s more is it uses less CPU power than the other file systems. It’s easy to recover data after a power failure and quite reliable. JFS: The file system JFS was created by IBM in 1990 and the name JFS is an acronym standing for Journaling File System, as we’ve already covered this concept with the number 3 file system in this article, you should already be quite familiar with what exactly this means. Thus, if you aren’t particularly keen on racking your brain between the different pros and cons of all the many file systems you can choose from, we definitely recommend you just go with this one. While it may not be the most cutting edge, it is absolutely reliable and stable – which is really valuable in Linux. Because this file system overcomes numerous limitations that the third extended system had, it is both widely used, and the default file system that most Linux distros use. Nowadays, there are so many better options to choose from that there’s hardly any reason to use this extended file system anymore either.Įxt4: ext4, standing for “fourth extended system”, was created in 2006.
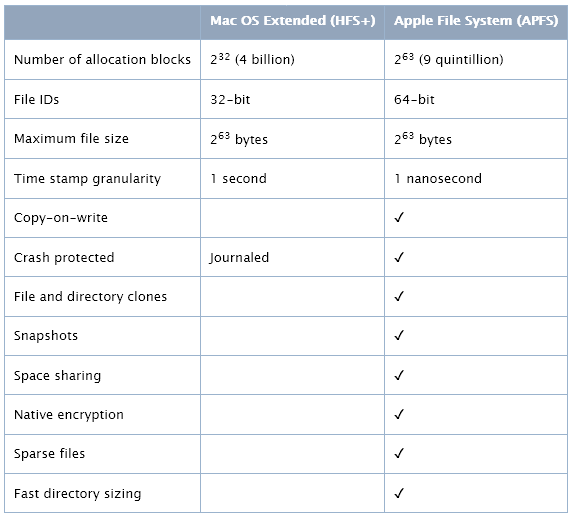
This means that if for some reason, the computer or hard disk(s) crash or experience some kind of power failure, this separate log containing the changes made before the crash can be used to access that stored data, thus repairing and restoring the files upon reboot.

A journaling file system is a system that records in a separate log changes and updates to files and data before such actions have been completed. Like ext, this file system is very old, so it really should just be avoided.Įxt3: ext3, or third extended system, created in 2001, surpasses ext2 in that it is a journaling file system. This file system notably allows for up to 2 TB of data. It innovated in areas such as storage capacity, and general performance. Created in 1993, ext2 was designed to be the successor of the original extension system for Linux. The purpose of its creation originally was to innovate beyond the file system used before it (the MINIX file system) and overcome its limitations.Īs this file system is about 30 years old at the time this article was written, many Linux distros no longer support it, so it is not really used anymore.Įxt2: also referred to as “second extended system”. Its functionality was designed partly based on the UNIX file system. We’ll delve into each one of these Linux File Systems and give a brief description.Įxt: “ext” is an acronym that stands for “extended file system” and was created in 1992 and is the very first file system designed specifically for Linux.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
